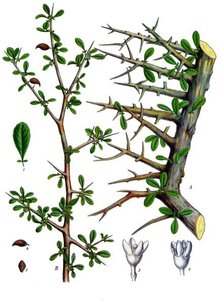
Chinese Pinyin: Mo Yao Latin: Commiphora Myrrha
Part of Herb Used: Gum Resin
Genus:
Traditional Chinese Medicinal (TCM) Uses:*
In traditional Chinese medicine, myrrh is classified as bitter and spicy, with a neutral temperature. It is said to have special efficacy on the heart, liver, and spleen meridians, as well as "blood-moving" powers to purge stagnant blood from the uterus. It is therefore recommended for rheumatic, arthritic, and circulatory problems, and for amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea, menopause, and uterine tumors.
Its uses are similar to those of frankincense, with which it is often combined in decoctions, liniments, and incense. When used in concert, myrrh is "blood-moving" while frankincense moves the Qi, making it more useful for arthritic conditions.
It is combined with such herbs as notoginseng, safflower petals, Angelica sinensis, cinnamon, and Salvia miltiorrhiza, usually in alcohol, and used both internally and externally.[7]1.*
References:
- Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Myrrh#Traditional_Chinese_medicine
Natural dietary supplements are designed to offer the body support to promote health, harmony, balance and overall well being.*

 Get Well Natural, LLC
Get Well Natural, LLC  Kidney Function & Regeneration Health
Kidney Function & Regeneration Health  Platelet & Blood Cell Health
Platelet & Blood Cell Health  Prostate, Flow & Function Health
Prostate, Flow & Function Health  General Mind & Body Health
General Mind & Body Health  Heart, Cholesterol & Cardio Health
Heart, Cholesterol & Cardio Health  Allergy-Free Body
Allergy-Free Body  Anxiety & Stress
Anxiety & Stress  Blood Platelet Counts & Function
Blood Platelet Counts & Function  Blood Pressure Health
Blood Pressure Health  Kidney Health
Kidney Health  Immune System Health & Balance
Immune System Health & Balance  Prostate & Urinary Health Function
Prostate & Urinary Health Function  Blood Sugar Balance
Blood Sugar Balance  Cardiovascular Heart Health
Cardiovascular Heart Health  Detoxification & Healthy Cells
Detoxification & Healthy Cells  Women's Health
Women's Health  Liver Regeneration
Liver Regeneration  Pain-Free Body
Pain-Free Body  Water & Air Filtration
Water & Air Filtration 


